Nội dung
If an asset is not used in any one year, then no depreciation will be charged for that year assuming that there is no decline in its service life. This method is suitable in case the use of asset varies from period to period. Here is a summary of the depreciation expense over time for each of the 4 types of expense. Activities Based Depreciation allows the management to match between revenue and depreciation expense.
She holds a Bachelor's degree from UCLA and has served on the Board of the National Association of Women Business Owners. She also regularly writes about travel, food, and books for various lifestyle publications. Therefore, Company A will depreciate the machine at the amount of $16,000 https://www.bookstime.com/articles/units-of-production-method annual for 5 years. Company ABC purchases a new Excavator that cost $ 220,000 for a construction project. The Southern company uses a delivery truck whose cost is $50,000 and the salvage value is zero. The company plans to retire the truck after it has been driven 250,000 miles.
Straight Line Depreciation Formula
We can calculate the activity method of deprecation by estimating the total output in the lifetime of the asset. And then calculate the cost per unit of output which is simply the purchase price less scrap value and divided by total output. Then we can get the depreciation expense per year by multiplying the output during the year with the cost per unit of output. Accumulated depreciation is the sum of depreciation expenses over the current and all prior years. The adjusted basis of your machine is the difference between the asset's net cost and the total accumulated depreciation. Total accumulated depreciation isn't allowed to exceed the machine's net cost, and it should equal the net cost of the machine.
- Depreciation is just an accounting method to show the expense of using an asset over time.
- The double-declining balance method results in higher depreciation expenses in the beginning of an asset's life and lower depreciation expenses later.
- However, tax regulations say you must spread the cost of that asset over its estimated useful life.
- Some companies may use the double-declining balance equation for more aggressive depreciation and early expense management.
It is easy to prepare a budget and project net profit during the period. As per the sum of years' formula, the depreciation for the machinery is $540,000 in the first year and $480,000 in the second year. Using the depletion method of depreciation, show the Mine Account for the above three years. Find out the depreciation for each of the six years under (a) Production Units Method and (b) Machine Hour Rate Method. Depreciation calculations determine the portion of an asset's cost that can be deducted in a given year. Or, it may be larger in earlier years and decline annually over the life of the asset.
Join PRO or PRO Plus and Get Lifetime Access to Our Premium Materials
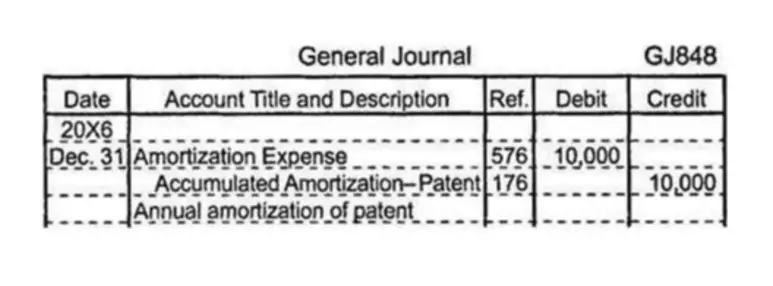
One common example is an asset on which you took a section 179 deduction. Your car loses value as you drive it more due to factors like it gets scratches/dents, https://www.bookstime.com/ it loses demand, etc. To record depreciation, you must make a journal entry debiting Depreciation Expense and crediting Accumulated Depreciation.
Other names used for activity method of depreciation are variable charge approach and units of output method. The activity-based depreciation method calculates an asset's depreciation cost based on its activity or usage. It differs from other depreciation methods that result in linear or inconsistent depreciation. However, it may require a company to estimate the asset's lifetime expected output. The activity-based depreciation method is not as common as the others mentioned above.
Why Should We Use Activity-Based Depreciation?
GAAP is a set of rules that includes the details, complexities, and legalities of business and corporate accounting. GAAP guidelines highlight several separate, allowable methods of depreciation that accounting professionals may use. Then, multiply that quotient by the number of units (U) used during the current year. Accountants use the straight line depreciation method because it is the easiest to compute and can be applied to all long-term assets. However, the straight line method does not accurately reflect the difference in usage of an asset and may not be the most appropriate value calculation method for some depreciable assets.
How do you calculate activity-based depreciation?
- Depreciable Base = Asset Cost – Salvage Value.
- Depreciation per Unit = Depreciable Base / Useful Units.
- Depreciation for Period = Number of Units Used in a Period Depreciation per Unit.